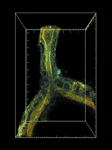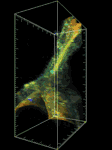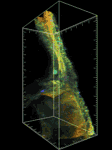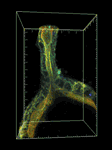
研究課題名:生体イメージングによる血管新生シグナルの時空間制御機構の解明
研究代表者(所属):福原茂朋(国立循環器病研究センター研究所 細胞生物学部)
研究内容

RhoファミリーG蛋白質は、細胞形態・運動において中心的な役割を持つシグナル分子であるので、内皮細胞の形態・運動制御におけるこれら分子の役割を明らかにする。具体的には、共鳴蛍光エネルギー移動の原理を基に開発された RhoファミリーG蛋白質バイオセンサーを、血管で特異的に発現するゼブラフィッシュを樹立し、生体蛍光イメージングを行うことで、RhoファミリーG蛋白質が内皮細胞の形態・運動を制御するメカニズムを解明する。また、細胞周期バイオセンサー Fucci を、血管で特異的に発現するゼブラフィッシュを樹立し、生きた個体の血管で内皮細胞周期を可視化できるシステムを構築する。これにより、血管形成における内皮細胞増殖の意義を明らかにする。
代表的論文3編
Vascular endothelial-cadherin stabilizes at cell-cell junctions by anchoring to circumferential actin bundles through α- and β-catenins in cyclic AMP-Epac-Rap1 signal-activated endothelial cells.
Noda, K., Zhang, J., *Fukuhara, S., Kunimoto, S., Yoshimura, M. and *Mochizuki, N.
Mol Biol Cell, 21, 584-596, (2010) *Co-corresponding authors
Differential function of Tie2 at cell-cell contacts and cell-substratum contacts regulated by angiopoietin-1.
*Fukuhara, S., Sako, K., Minami, T., Noda, K., Kim, H.Z., Kodama, T., Shibuya, M., Takakura, N., Koh, G.Y. and *Mochizuki, N.
Nat Cell Biol, 10, 513-526, (2008) *Co-corresponding authors
Cyclic AMP potenciates VE-cadherin–mediated cell-cell contact to enhance endothelial barrier function through an Epac-Rap1 signaling pathway.
Fukuhara, S., Sakurai, A., Sano, H., Yamagishi, A., Somekawa, S., Takakura, N., Saito, Y., Kangawa, K. and Mochizuki, N.
Mol Cell Biol, 25, 136-146, (2005)